ZDIN-Zahlen im Detail
Das umfangreiche ZDIN-Netzwerk aus Wissenschaft und Wirtschaft spannt sich über ganz Niedersachsen. Gemeinsam verzeichnen die Zukunftslabore und die Koordinierungsstelle beeindruckende Projekterfolge, die auf dieser Seite im Detail vorgestellt werden.
Wissenschaftliche Veröffentlichungen
With rising electricity demand through digitization and innovation, the urgency of climate change mitigation, and the recent geopolitical crisis, stakeholders in developing countries face the complex ...
With rising electricity demand through digitization and innovation, the urgency of climate change mitigation, and the recent geopolitical crisis, stakeholders in developing countries face the complex task to build reliable, affordable, and low-emission energy systems. Information inaccessibility, data unavailability, and scarce local expertise are major challenges for planning and transitioning to decentralized solutions. Motivated by the calls for more solution-oriented research regarding sustainability, we design, develop, and evaluate the web-based decision support system NESSI4Dweb+ that is tailored to the needs and capabilities of various stakeholders in developing countries. NESSI4Dweb+ is open access and considers location-specific circumstances to facilitate multi-energy planning. Its applicability is demonstrated with a case study of a representative rural village in southern Madagascar and evaluated through seven interviews with experts and stakeholders. We show that NESSI4Dweb+ can support the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and enable the very prerequisite of digitization: reliable electrification.
Autor*innen
- M. Sc. Maria Hart (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Michael H. Breitner (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: Energy Informatics
- Datum: 20.12.2022
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
The black-box nature of Artifcial Intelligence (AI) models and their associated explainability limitations create a major adoption barrier. Explainable Artifcial Intelligence (XAI) aims to make AI mod ...
The black-box nature of Artifcial Intelligence (AI) models and their associated explainability limitations create a major adoption barrier. Explainable Artifcial Intelligence (XAI) aims to make AI models more transparent to address this challenge. Researchers and practitioners apply XAI services to explore relationships in data, improve AI methods, justify AI decisions, and control AI technologies with the goals to improve knowledge about AI and address user needs. The market volume of XAI services has grown signifcantly. As a result, trustworthiness, reliability, transferability, fairness, and accessibility are required capabilities of XAI for a range of relevant stakeholders, including managers, regulators, users of XAI models, developers, and consumers. We contribute to theory and practice by deducing XAI archetypes and developing a user-centric decision support framework to identify the XAI services most suitable for the requirements of relevant stakeholders. Our decision tree is founded on a literature-based morphological box and a classifcation of real-world XAI services. Finally, we discussed archetypical business models of XAI services and exemplary use cases.
Autor*innen
- Paul Hoppe (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- Sarah Jagels (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- Luisa Licker (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Michael H. Breitner (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: Electronic Markets
- Datum: 23.11.2022
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
The existence of voltage range violations represents a challenge in low voltage grids with a high penetration of decentralized generation, storage capacities or electro-mobility. If grid expansion is ...
The existence of voltage range violations represents a challenge in low voltage grids with a high penetration of decentralized generation, storage capacities or electro-mobility. If grid expansion is to be avoided in the future, an extensive information exchange between the system’s components is required to provide an optimal energy supply and guarantee operating requirements. This can be studied in details by modelling the energy system components and the communication between them, which is one of the aims of the research project "Future Energy Laboratories". Highly integrated application scenarios for sample districts in Germany are simulated and thoroughly analysed during the project. For the detection and correction of voltage range violations at individual buses of a grid, an Open Source Grid Observer tool was developed and tested as a flexibility feature in a quasi-dynamic energy system simulation of a residential district. It allows a wide range of compatibility between various simulation scenarios, as it gives recommendations for power control at considered buses according to predefined flexibilities, such as the type of power (active or reactive), flexibility components (e.g. generation and storage) and injection increment. The corrections were calculated using two methods of the voltage sensitivity analysis theory. A comparison between the methods’ robustness, accuracy and calculation speed is presented, being important performance factors to be considered in this kind of simulations. The functionality of the tool is demonstrated in scenarios with temporary peak loads from electric vehicle charging or a high share of distributed photovoltaic power generation.
Autor*innen
- Sarah Fayed (Hochschule Emden/Leer)
- Fernando Andres Penaherrera Vaca (OFFIS Institut für Informatik, FuE-Bereich Energie)
- Henrik Wagner (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Prof. Dr. Johannes Rolink (Hochschule Emden/Leer, Abteilung Elektrotechnik und Informatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: 2022 10th International Conference on Smart Grid and Clean Energy Technologies (ICSGCE)
- Datum: 14.10.2022 - 16.10.2022
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
International politics (Glasgow Climate Agreement) and German politics (Climate Protection Act) recently tightened their targets for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The German target of reduc ...
International politics (Glasgow Climate Agreement) and German politics (Climate Protection Act) recently tightened their targets for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The German target of reducing GHG emissions by 65% until 2030 particularly affects the transport sector, which contributed 19% of total emissions in 2021. Battery-electric mobility represents the most promising post-fossil mobility approach as the number of electric vehicles (EV) worldwide has grown exponentially in recent years. Parallel to the increase in vehicle counts, the number of charging points and the corresponding charging infrastructure must to grow as well. The increased load from these charging processes was unknown while planning and building the electric grid of existing districts and nowadays may cause violations of operational boundaries. The goal of this research is to analyze effects and impacts of an increasing EV penetration rate on the lowvoltage grid in an existing district in Lower Saxony and identify the maximum possible grid capacity for EV charging. Identified limiting factors are then considered in multiple scenarios. Opportunities for different levels of cooperative energy generation, storage and smart charging strategies are applied to enhance the grid’s capacity for EV. The simulation scenarios, the used models (self-developed and modified existing ones) will be accessible under open-source license enabling a transparent research process and improving research quality and accessibility. Researchers therefore will be able to extend the co-simulation with their own models or implement and examine various other districts and communities. Due to the multidisciplinary nature of the components involved in the simulation of the district, a co-simulation framework is beneficial to conduct the power system analyses. The co-simulation framework mosaik allows coupling different simulation tools and models enabling the orchestration and communication of parameters between components, so that a systems-wide perspective is achieved. The components of the districts’ energy system are modeled object-orientated in Python, allowing setting individual properties for each component. Control methods exist as separate models (e.g. district energy management system) and as part of components (e.g. smart charging in charging station model). The grid electricity demand of EV is calculated from empirical data using the Emobpy tool. Mosaik orchestrates all data flows and initializes a Pandapower grid model to perform power flow calculations in each timestep forming quasi-dynamic load flow calculations. The results are processed in a self-developed grid observer and validated in accordance with applicablestandards to determine the grid capacity for EV. In multiple scenarios different combinations of renewable energy system models and control models are simulated to increase grid capacity and prevent critical grid situations for high EV penetration rates.
Autor*innen
- Henrik Wagner (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Fernando Andres Penaherrera Vaca (OFFIS Institut für Informatik, FuE-Bereich Energie)
- Sarah Fayed (Hochschule Emden/Leer)
- M.Sc. Oliver Werth (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Engel (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Michael H. Breitner (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung Energieinformatik)
- Prof. Dr. Johannes Rolink (Hochschule Emden/Leer, Abteilung Elektrotechnik und Informatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: 6th E-Mobility Power System Integration Symposium 2022
- Datum: 10.10.2022
The implementation of the smart grid and the related use cases requires the interaction of a wide variety of systems from many manufacturers. The selection of suitable communication protocols is a key ...
The implementation of the smart grid and the related use cases requires the interaction of a wide variety of systems from many manufacturers. The selection of suitable communication protocols is a key factor in achieving the necessary interoperability and avoiding vendor lock-ins. Considering the large number of possible protocols, this selection process is becoming increasingly difficult and time-consuming. To simplify and accelerate this process, the use of a morphological box is presented. The partial aspects defined in the morphological box are chosen in such a way that they can describe both the requirements of a use case and the possibilities of the protocol under assessment. Applying the box eventually results in reusable profiles that allow the comparison of use cases and protocols in a quick and simple way. The utilization is demonstrated by evaluating the MQTT protocol for the realization of a given use case.
Autor*innen
- M.Sc. Sebastian Hanna (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Sebastian Rohjans (OFFIS Institut für Informatik, FuE-Bereich Energie)
- M.Eng. Philipp Heeren (Hochschule Emden/Leer)
- Prof. Dr. Johannes Rolink (Hochschule Emden/Leer, Abteilung Elektrotechnik und Informatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: IEEE PES ISGT Europe 2022; Novi Sad, Republic of Serbia
- Datum: 10.10.2022 - 12.10.2022
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
Wissenschaftliche Vorträge
Referent*innen
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 43. International Conference on Information Systems
- Datum: 12.12.2022
Referent*innen
- Sarah Fayed (Hochschule Emden/Leer)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 10th International Conference on Smart Grid and Clean Energy Technologies (ICSGCE 2022)
- Datum: 15.10.2022
Referent*innen
- Henrik Wagner (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 6th E-Mobility Power System Integration Symposium 2022 in Den Haag, Niederlande
- Datum: 10.10.2022
Referent*innen
- M.Sc. Oliver Werth (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
- M. Sc. Stephan Ferenz (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Department für Informatik)
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 17th International Conference on Wirtschaftsinformatik
- Datum: 21.09.2022
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: ACM e-Energy 2022
- Datum: 29.06.2022
Außerwissenschaftliche Beiträge
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Lars Kühl (Ostfalia Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften, Institut für Energieoptimierte Systeme (EOS))
Beitrag
- Anlass: WOW! Pop up Veranstaltung
- Datum: 15.12.2022 - 15.12.2022
Referent*innen
- M.Sc. Tim Brauner (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
Beitrag
- Anlass: Leibniz AnsprechBAR: Der Tag der offenen Tür der Leibniz Universität
- Datum: 05.11.2022 - 05.11.2022
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
Beitrag
- Anlass: 4. Thüringer KI-Forum
- Datum: 04.11.2022
Referent*innen
- Henrik Wagner (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
Beitrag
- Anlass: Meet the Scientist im phaeno Wolfsburg
- Datum: 11.09.2022 - 11.09.2022
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
Beitrag
- Anlass: Keynote beim Best Practice Gipfel "Klimaneutrale Produktion & Digitalisierung" des VDMA
- Datum: 12.07.2022 - 12.07.2022
Messebeiträge
Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität | OFFIS – Institut für Informatik) nahm neben weiteren Teilnehmer*innen an der Podiumsdiskussion zum Thema "Digitale Transparenz stärken – mit KI! Beispiele aus der Energie-, Gesundheits- und Produktionsbranche" teil.
Beteiligte ZDIN-Einrichtungen
- OFFIS Institut für Informatik
- FuE-Bereich Energie
Beitrag
- Art des Beitrags: Podiumsdiskussion
- Datum: 13.09.2022
- Ort: Hannover
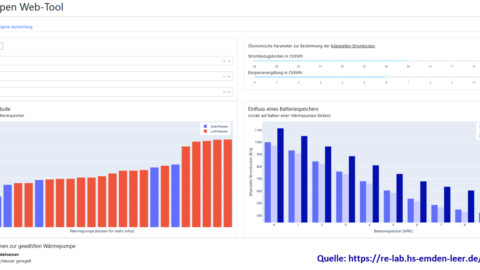
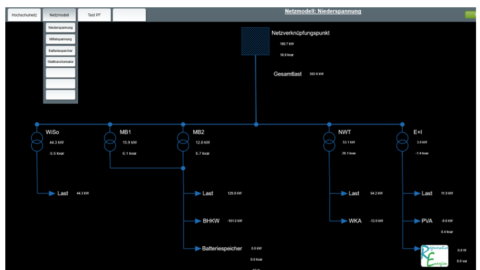
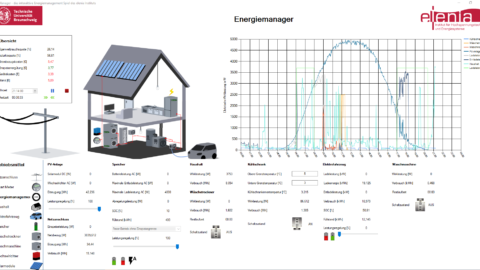
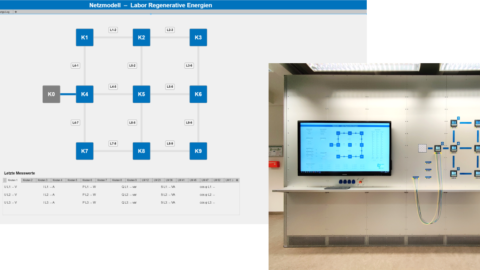
Technologiedemonstratoren
Transfer-Workshops
Nach dem Workshop im letzten Jahr wurden die Erfahrungen aus der Laborkopplung RE-LAB (HSEL) und NESTEC (DLR) in den erfolgten Konstellationen und Einrichtungen von laborverbindender Hard- und Software sowie Testmethoden zu deren funktionalen Überprüfung diskutiert. Die Simulations- und Kopplungsframeworks und anbindungsfähige Hardwareemulation wurde für eine erweiternde Kopplung abgeglichen und bestimmt. Die wissenschaftlichen Laborverantwortlichen aus den ZLE Partnerinstitutionen diskutierten und vereinbarten einen engeren Austausch und Arbeitsschritte für die gezielte Kopplung von NESTEC mit dem Living LAB SESA (OFFIS).
Nach den erfolgreichen Testes zwischen HS-EL und DLR wird nun die Einbindung des Living Lab SESA vom OFFIS vorangetrieben. Aufbauend auf bisherige Erfahrungen wurde sich auf eine Auswahl genutzter Tools und Frameworks und geeinigt. Ein Folgeworkshop findet nach ersten Vorarbeiten und Tests im Frühjahr 2023 statt.
Workshop
- Datum: 20.07.2022
- Ort: online
Fort- und Weiterbildungen
Studienabschlussarbeiten
- Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung Energieinformatik)
- Art: Master
- Themencluster: Modellierung und Simulation
- Datum: 16.12.2022
- Art: Master
- Themencluster: Künstliche Intelligenz
- Datum: 05.12.2022 - 05.06.2023
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Engel (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Henrik Wagner (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Art: Master
- Themencluster: Modellierung und Simulation
- Datum: 01.12.2022 - 29.05.2023
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- Art: Bachelor
- Themencluster: Künstliche Intelligenz
- Datum: 01.12.2022
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Engel (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Art: Studienarbeit (min. 14 Credits)
- Themencluster: Modellierung und Simulation
- Datum: 30.11.2022 - 31.03.2023