ZDIN-Zahlen im Detail
Das umfangreiche ZDIN-Netzwerk aus Wissenschaft und Wirtschaft spannt sich über ganz Niedersachsen. Gemeinsam verzeichnen die Zukunftslabore und die Koordinierungsstelle beeindruckende Projekterfolge, die auf dieser Seite im Detail vorgestellt werden.
Wissenschaftliche Veröffentlichungen
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based methods in the energy sector challenge companies, organizations, and societies. Organizational issues include traceability, certifiability, explainability, responsib ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based methods in the energy sector challenge companies, organizations, and societies. Organizational issues include traceability, certifiability, explainability, responsibility, and efficiency. Societal challenges include ethical norms, bias, discrimination, privacy, and information security. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) can address these issues in various application areas of the energy sector, e.g., power generation forecasting, load management, and network security operations. We derive Key Topics (KTs) and Design Requirements (DRs) and develop Design Principles (DPs) for efficient XAI applications through Design Science Research (DSR). We analyze 179 scientific articles to identify our 8 KTs for XAI implementation through text mining and topic modeling. Based on the KTs, we derive 15 DRs and develop 18 DPs. After that, we discuss and evaluate our results and findings through expert surveys. We develop a Three-Forces Model as a framework for implementing efficient XAI solutions. We provide recommendations and a further research agenda.
Autor*innen
- Sarah K. Lier (Leibniz Universität Hannover)
- Prof. Dr. rer. nat. habil. Michael H. Breitner (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: International Conference on Information Systems
- Datum: 10.12.2023
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
Power grids must be stable and reliable, but the growing importance of intelligent control in smart grids creates new challenges due to the increasing dependence on communication networks. This paper ...
Power grids must be stable and reliable, but the growing importance of intelligent control in smart grids creates new challenges due to the increasing dependence on communication networks. This paper investigates the influence of communication on power systems in a future scenario. The simulation environment contains a power grid of a medium-sized city in northwest Germany, in the year 2035, where the normal operation of the power system is disturbed by increased communication traffic. The power and communication networks are integrated into a co-simulation environment, that implements smart grid services in an agent-based control structure. In a case study, multiple scenarios are compared that differ in the configuration of the communication network, to show how the simulation environment can be used to study the interactions between power and communication networks.
Autor*innen
- B.Sc. Malin Radtke (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Christoph Stucke (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg)
- Malte Trauernicht (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg)
- Carsten Montag
- M. Sc. Frauke Oest (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- M. Sc. Emilie Frost (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- Dr. Jörg Bremer
- Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung Energieinformatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: 2023 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI)
- Datum: 05.12.2023 - 08.12.2023
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
In the last ten years Germany has met less than half of its renovation quota annually. This study aims to create a roadmap for German renovation by identifying the construction era of single-family ho ...
In the last ten years Germany has met less than half of its renovation quota annually. This study aims to create a roadmap for German renovation by identifying the construction era of single-family homes which has the greatest potential for decarbonization. A multi-objective optimization was conducted which varied the building envelope and energy systems while optimizing for annual cost and carbon emissions. The optimization was carried out in oemof.solph and PyGMO on typical German building stocks from 11 different construction eras between 1860 and 2020. The buildings were modelled in TEASER using TABULA building stock data. It was found that by spending the same amount of money annually as the business as usual case, the post-war construction era represents the highest potential for improvement. Additionally, if all construction eras are fully renovated from before 2008 over 90 megatons of CO2 emissions could be saved annually. Lastly, the electrification of the energy system and removal of fuel-based energy production was the primary outcome for both the most ecologic and most economic Pareto solutions, across all construction eras.
Autor*innen
- Cody Hancock (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Dr. Peter Klement (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Lucas Schmeling (KEHAG Energiehandel GmbH)
- Dr. Benedikt Hanke (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Dr. Karsten von Maydell (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: Energiewendebauen 14
- Datum: 09.11.2023
Energy market rules should incentivize market participants to behave in a market and grid conform way. However, they can also provide incentives for undesired and unexpected strategies if the market d ...
Energy market rules should incentivize market participants to behave in a market and grid conform way. However, they can also provide incentives for undesired and unexpected strategies if the market design is flawed. Multi-agent Reinforcement learning (MARL) is a promising new approach to predicting the expected profit-maximizing behavior of energy market participants in simulation. However, reinforcement learning requires many interactions with the system to converge, and the power system environment often consists of extensive computations, e.g., optimal power flow (OPF) calculation for market clearing. To tackle this complexity, we provide a model of the energy market to a basic MARL algorithm in the form of a learned OPF approximation and explicit market rules. The learned OPF surrogate model makes an explicit solving of the OPF completely unnecessary. Our experiments demonstrate that the model additionally reduces training time by about one order of magnitude but at the cost of a slightly worse performance. Potential applications of our method are market design, more realistic modeling of market participants, and analysis of manipulative behavior.
Autor*innen
- M.Sc. Thomas Wolgast (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: arXiv
- Datum: 01.11.2023
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is vital for the operation of modern power systems, giving rise to Cyber-Physical Energy Systems (CPESs). ICT enables the grid services (GSs) needed for ...
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is vital for the operation of modern power systems, giving rise to Cyber-Physical Energy Systems (CPESs). ICT enables the grid services (GSs) needed for monitoring and controlling the physical parameters of the power system, especially for remedying the impact of disturbances. But the ICT integration makes the overall system more complex, leading to new and unforeseen disturbances. This motivates the need for a resilient system design capable of absorbing and recovering from such disturbances. The current state of the art lacks a comprehensive resilience assessment of ICT-enabled GSs in CPESs. To address this, a novel method and metrics to assess the resilience of GSs in CPESs are presented in this paper. An operational state model of a GS, with three states, i.e., normal, limited and failed, is used to capture its performance, which is essential for quantifying its resilience. Sequential Monte Carlo simulations are performed with the model to capture the behaviour of ICT components to compute the operational state trajectory of the GSs. Metrics are then derived to quantify the resilience and its constituting phases. The method is demonstrated using two ICT system designs for the CIGRE MV benchmark grid, considering the state estimation as an exemplary GS. The simulation results show that the proposed method can capture the differences between ICT system designs with regard to resilience metrics. The contribution can, therefore, be used to analyse, compare and potentially improve the resilience of ICT system designs for CPES.
Autor*innen
- Anand Narayan
- M.Sc. Michael Brand (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung Energieinformatik)
Veröffentlichung
- Im Rahmen des Buches/Journals bzw. Konferenz: Energy Informatics
- Datum: 19.10.2023
- Link zur Veröffentlichung
Wissenschaftliche Vorträge
Referent*innen
- Sarah K. Lier (Leibniz Universität Hannover)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: International Conference on Information Systems
- Datum: 12.12.2023
Referent*innen
- B.Sc. Malin Radtke (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Christoph Stucke (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg)
- Malte Trauernicht (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg)
- Carsten Montag
- M. Sc. Frauke Oest (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- M. Sc. Emilie Frost (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- Dr. Jörg Bremer
- Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung Energieinformatik)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 2023 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI)
- Datum: 06.12.2023
Referent*innen
- Cody Hancock (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Dr. Peter Klement (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Lucas Schmeling (KEHAG Energiehandel GmbH)
- Dr. Benedikt Hanke (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Dr. Karsten von Maydell (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: Energiewendebauen 14
- Datum: 09.11.2023
Referent*innen
- Alexander Hill
- Jan-Hendrik Bruhn
- Christian Pieper
- Dr. Patrik Schönfeldt (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR))
- Fernando Andres Penaherrera Vaca (OFFIS Institut für Informatik, FuE-Bereich Energie)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 12th DACH+ Conference on Energy Informatics 2023
- Datum: 05.10.2023
Referent*innen
- Sarah Fayed (Hochschule Emden/Leer)
Vortrag
- Im Rahmen der Veranstaltung: 22nd Wind and Solar Integration Workshop (WIW 2023)
- Datum: 28.09.2023
Außerwissenschaftliche Beiträge
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- M. Sc. Stephan Ferenz (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Department für Informatik)
Beitrag
- Anlass: EWB-Stunde (Energiewendebauen)
- Datum: 07.12.2023
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- M.Sc. Stefanie Holly
Beitrag
- Anlass: energy@lunch
- Datum: 29.11.2023
Referent*innen
Beitrag
- Anlass: Das Ende des Verbrennungsmotors: Warum sich E-Autos schneller etablieren werden
- Datum: 07.11.2023 - 07.11.2023
Referent*innen
- M. Sc. Maria Hart (Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik)
Beitrag
- Anlass: Die Nacht, die Wissen schafft 2023
- Datum: 04.11.2023 - 04.11.2023
Referent*innen
- Prof. Dr. Sebastian Lehnhoff (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung Energieinformatik)
Beitrag
- Anlass: Kontaktpunkt Wirtschaft
- Datum: 01.11.2023
Messebeiträge
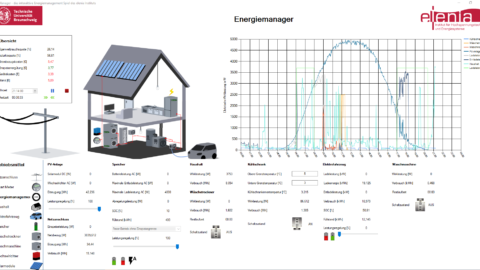
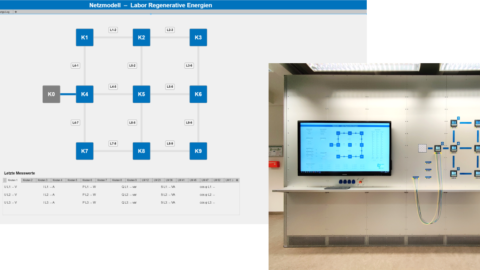
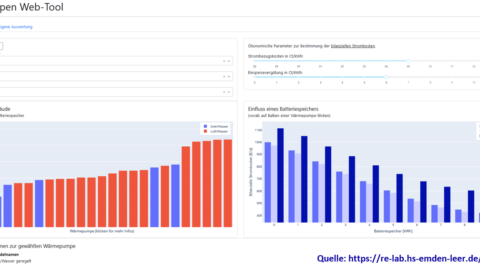
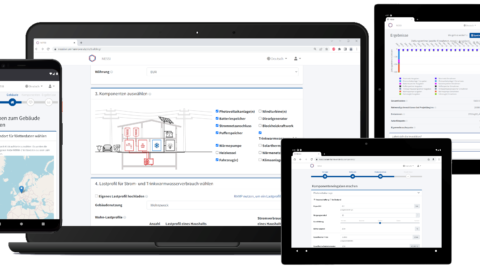
Das Zukunftslabor Energie präsentierte auf dem Gemeinschaftsstand Niedersachsen das Webtool NESSI (Nano Energy System Simulator). Es unterstützt Hauseigentümer*innen, Vermieter*innen und Unternehmen dabei, passende erneuerbare Energietechnologien zu finden, um Energie im Gebäude- und Mobilitätssektor einzusparen.
Beteiligte ZDIN-Einrichtungen
- Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg
- Department für Informatik
- Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (DLR)
- Institut für vernetzte Energiesysteme e.V. (Oldenburg)
- Hochschule Emden/Leer
- Fachbereich Technik
- Leibniz Universität Hannover
- Institut für Wirtschaftsinformatik
- Technische Universität Braunschweig
- elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme
- Ostfalia Hochschule für angewandte Wissenschaften
- Institut für Energieoptimierte Systeme (EOS)
- OFFIS Institut für Informatik
- FuE-Bereich Energie
Beitrag
- Art des Beitrags: Demonstratoren
- Datum: 17.04.2023
- Ort: Hannover
Technologiedemonstratoren
Transfer-Workshops
Fort- und Weiterbildungen
- Sarah Fayed (Hochschule Emden/Leer)
- Angebotsart: Seminar
- Datum: 13.11.2023 - 15.01.2024
Studienabschlussarbeiten
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- M. Sc. Stephan Ferenz (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Department für Informatik)
- Art: Master
- Themencluster: Datenmanagement und -analyse
- Datum: 20.12.2023
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- M. Sc. Stephan Ferenz (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Department für Informatik)
- Art: Bachelor
- Themencluster: Datenmanagement und -analyse
- Datum: 20.12.2023
- Henrik Wagner (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Bernd Engel (Technische Universität Braunschweig, elenia Institut für Hochspannungstechnik und Energiesysteme)
- Art: Studienarbeit (min. 14 Credits)
- Themencluster: Modellierung und Simulation
- Datum: 15.12.2023 - 15.04.2024
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- Dr. rer. nat. Martin Tröschel (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Art: Bachelor
- Themencluster: IT-Plattformen und Cloud
- Datum: 12.12.2023
- Prof. Dr.-Ing. Astrid Nieße (Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, Abteilung für Digitalisierte Energiesysteme)
- Dr. rer. nat. Martin Tröschel (OFFIS Institut für Informatik)
- Art: Bachelor
- Themencluster: IT-Plattformen und Cloud
- Datum: 12.12.2023